Thyroid Cancer – Silent Signs, Diagnosis, and Management
Thyroid cancer is the result of the abnormal growth of cells in the thyroid gland – a butterfly-shaped gland located at the base of the neck. This gland produces hormones that help in the regulation of blood pressure, heart rate, and body temperature. Although thyroid cancer does not show any symptoms in the beginning, as the condition worsens, one may experience difficulty swallowing. Keep reading to learn more about the other silent signs of thyroid cancer.
Silent signs of thyroid cancer
In most cases, during the early onset of the condition, patients may not experience any symptoms. However, it can be discovered during a routine neck examination or an imaging scan aimed at another health problem. Furthermore, one cannot feel the thyroid gland by touch, but cancerous growth may cause a lump in the area. The other silent signs to look for are:
Neck pain
One of the rare signs of the condition is neck pain. In most cases, the pain may start in the front of the neck. However, some patients have also experienced neck pain extending to the ears. Hence, it’s suggested to look out for this particular symptom and if noticed, seek professional advice at the earliest.
Changes in the voice
A two-lobed gland that wraps around the larynx (voice box), the thyroid cartilage makes up the front part of the larynx. Multiple studies have shown that the larynx tissue contains special receptors that bind with or react to changes in thyroid-produced hormones. Hence, even the mildest changes in the gland may lead to changes in the voice. This can include hoarseness, changes in the loudness of voice, and sometimes even changes in how high or low the voice may sound. This happens due to the growth of nodules in and around the thyroid gland, leading to changes in its shape and pressure on the larynx.
Shortness of breath
One of the most common yet ignored symptoms of thyroid cancer is shortness of breath or dyspnea. This issue usually occurs in patients where the physical obstruction of the enlarged thyroid gland puts immense pressure on the esophagus and trachea (windpipe). Furthermore, this can also lead to general difficulty in breathing. Many patients report the breathing issue feels similar to breathing in air through a straw. Hence, causing them to gasp for air or work harder in order to breathe normally.
Difficulty swallowing
Difficulty swallowing, also known as dysphagia, is also one of the common symptoms reported in the early stages of thyroid cancer. This happens as a result of enlargement of the thyroid gland, leading to a compressed esophagus. Furthermore, patients experiencing difficulty swallowing may even experience compression symptoms, such as a sensation of food getting stuck in the throat and in rare cases, even choking. Additionally, studies have concluded that nodule size and lobe size directly affect the ability to swallow.
Diagnosis and treatment of thyroid cancer
Diagnosis
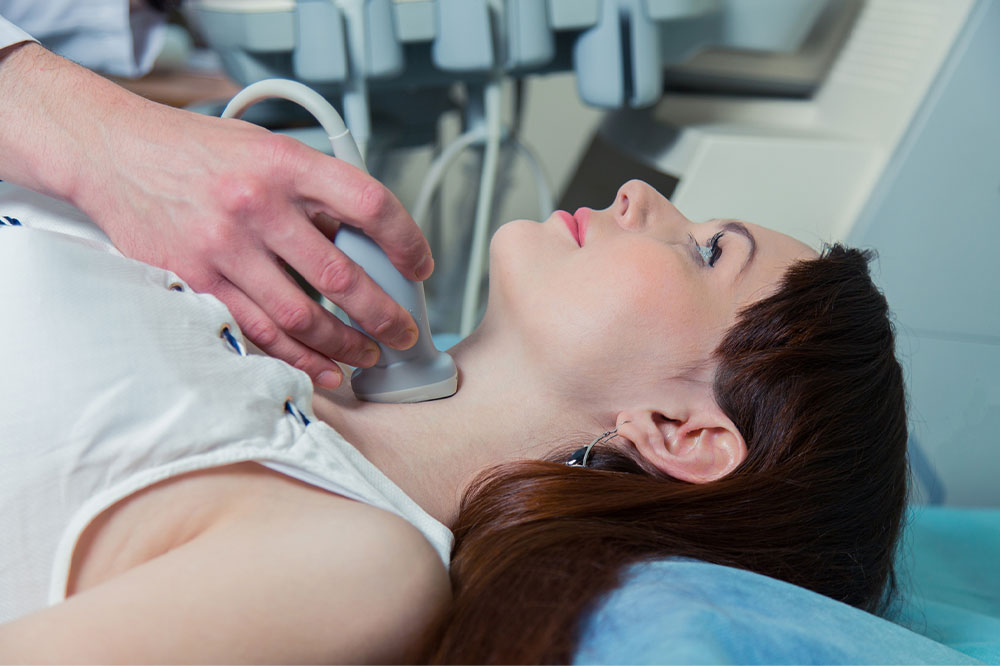
An evaluation for thyroid cancer usually begins with a physical exam. This is followed by a review of all the symptoms and diagnostic blood tests to check the functioning of the thyroid gland. Moreover, in some cases, healthcare professionals may also recommend a fine needle biopsy to identify the nature of the abnormality. The procedure involves the analysis of the tissue for cancer cells and other problems.
In addition to the above, imaging studies such as ultrasound and CT scans prove valuable in the determination of the spread of cancer cells and their associated treatment.
Treatment
The treatment of the condition usually depends on the type of cancer, its stage, and the overall health of the patient. One of the leading cancer centers in the world, the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSK) suggests treatment alternatives depending on the type of thyroid cancer and the preferences and needs of the patient. That said, these treatment alternatives may depend on various factors, such as:
Size of the tumor
Spread of the tumor outside the thyroid gland
Genomic analysis of the tumor
Overall health
After careful consideration of the above-mentioned factors, doctors may suggest a few treatment alternatives, such as:
Surgery
In most cases, the doctors may suggest the removal of the thyroid gland, also known as thyroidectomy, when the size of the tumor begins to affect the functioning of other bodily systems. However, in the case of small-size tumors, doctors may also advise partial removal of the thyroid gland – only the side with the tumor is removed (lobectomy). In cases where thyroid cancer patients have swollen lymph nodes with signs of cancer spread, the lymph nodes are removed as well. This effectively reduces the risk of recurrence of cancer in the neck area.
Radioactive Iodine Treatment (RAI)
As the thyroid gland absorbs all the iodine in the body, RAI can be effectively used as a treatment alternative for thyroid cancer. In this form of treatment, the patient has to take RAI in a capsule form where the remedy destroys the cancerous growths via radiation. However, this has little effect on other parts of the body and is a treatment that is often used to completely destroy cancerous cells.
Targeted Therapy
Targeted therapy involves the usage of kinase inhibitors. The kinases are proteins found inside the cells and help relay signals. This can also include signals for cell growth. Hence, in the case of advanced stages of thyroid cancer, doctors suggest targeted therapy to block certain kinases and help in the treatment of cancer.
In addition to the above, doctors may also suggest external beam radiation therapy to destroy the tumor. In this form of treatment, a carefully focused beam of radiation is delivered from outside the body to destroy cancer cells or slow down their growth.
Since thyroid cancer can drastically change one’s quality of life, individuals at risk of the condition are advised to keep an eye out for the symptoms. Doing so can ensure timely diagnosis and treatment.
















