Foods to manage Parkinson’s and treatment options

Parkinson’s is a neurological disorder that results in involuntary and unpredictable movements in the body, such as rigidity, tremors, and impaired balance and coordination. As the disease advances, these symptoms typically become more severe. Although there is currently no known cure for Parkinson’s, there are various strategies for managing the condition. Proper nutrition is a critical component of effective management, so consider the following dos and don’ts of nutrition and some promising new treatment options to explore.
Role of nutrition
While nutrition is important in general for a healthy life, those dealing with Parkinson’s should especially be careful of foods to eat and avoid. This is due to the complications that arise because of the disease. These can include complications like constipation. Due to the slowdown of the digestive system, constipation can be a regular occurrence in those suffering from this disease. Irregular bowel movements can be uncomfortable, but if constipation becomes severe, it can have a significant impact on the large intestine.
Dehydration is another common concern of Parkinson’s patients, so extra care needs to be given to hydration needs. Dehydration can cause dizziness, tiredness, confusion, weakness, and kidney issues.
When undergoing Parkinson’s treatment therapy, it is recommended to avoid high-protein meals. This is because it can cause the small intestine to overwork, leading to potential complications.
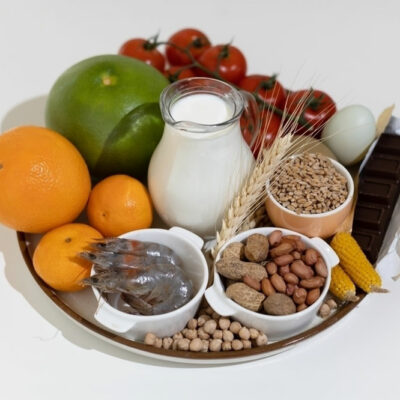
Foods to eat
Here are some foods and food groups one can incorporate in one’s meals to manage the disease.
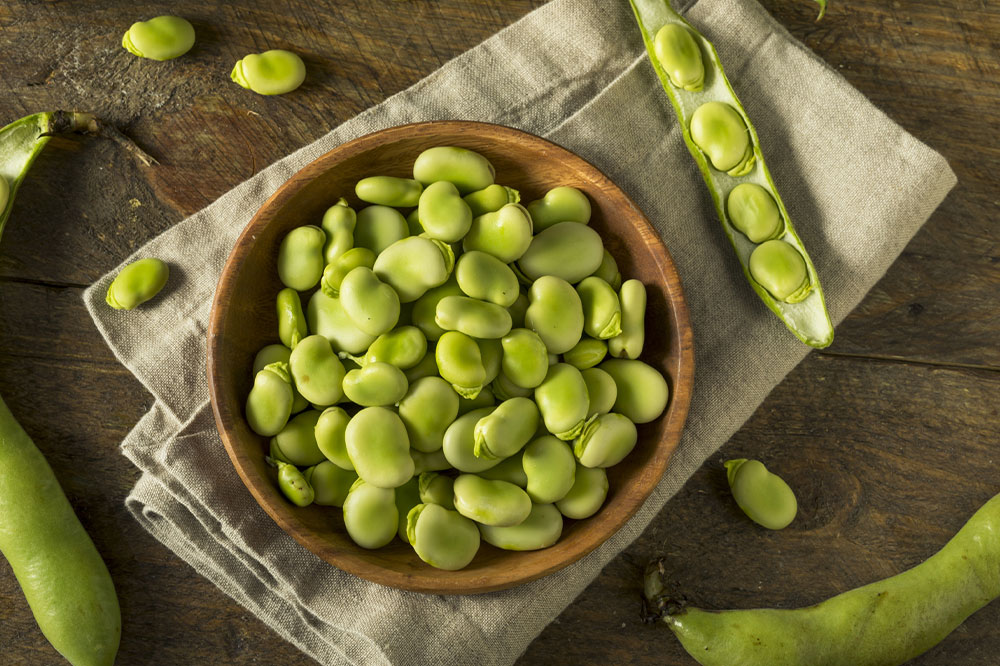
Fava beans
Also known as broad beans, these beans are rich in a compound called levodopa. Levodopa is known to be a compound used in Parkinson’s treatment therapies and has helped in the management of the symptoms of the disease. It is suggested that increased levodopa and carbidopa in the blood can be linked with improved muscle movement performance.
Salmon
Doctors often advise people with Parkinson’s to include omega-3-rich foods in their meal plans. These foods include salmon, halibut, oysters, soybeans, kidney beans, and flaxseeds, which can help manage the symptoms. These are healthy fats that are responsible for improving brain function and can also help those with Parkinson’s. There are studies to suggest the same and promote eating Omega 3-rich foods, which protect against most neurodegenerative diseases and not just Parkinson’s.
Berries
Blueberries, blackberries, goji berries, cranberries, and elderberries are all rich in antioxidants. According to research, foods rich in antioxidants should be eaten when managing Parkinson’s. These antioxidants protect against the oxidative stress caused in the body, which is common in Parkinson’s and is known to benefit brain function. Some other antioxidant-rich foods one can include are walnuts, brazil nuts, pecans, pistachios, and green leafy vegetables like kale and spinach. Nightshade vegetables like tomatoes, peppers, and eggplant are also great sources of antioxidants.
Studies suggest that a Mediterranean meal plan may be the best type of nutrition for those dealing with Parkinson’s. This includes eating more fruits, vegetables, whole grains, seeds, nuts, olive oil, and all plant-based foods. It is also recommended to consume seafood, dairy, chicken, and eggs in moderation while limiting the intake of red meat and sugary treats like candy, cookies, and other artificial sweets.
Specific nutrients to take
Research has shown that many individuals with Parkinson’s disease are deficient in certain nutrients, which can lead to malnourishment. Therefore, it is crucial to monitor for these deficiencies and consume the appropriate foods to treat them.
Those who are iron deficient should consume more spinach, tofu, beef, and fortified breakfast cereals.
Those with a vitamin B1 deficiency would benefit from eating more pork, lentils, peas, and beans.
Individuals with zinc deficiency should incorporate more whole grains, red meat, chicken, and oysters into their meal plan.
Those with a Vitamin D deficiency can find relief by consuming salmon, tuna fish, fortified dairy products, and cod liver oil.
Calcium deficiency can be addressed by consuming more dairy products, green leafy vegetables, and fortified soy products.
Foods to avoid
Certain food groups should be avoided as they can worsen the symptoms of the disease and one’s overall health.
Fried foods
These are foods that are high in saturated fats. Studies suggest that those with high consumption of saturated fats are more likely to suffer from chronic conditions like heart disease and even diabetes. It may be impossible to eliminate them from the foods altogether, so they should only rarely be added after consultation with the doctor. Some of the foods in this category include fried chicken, fried potatoes, beef, lard, cheese, butter, and even palm oil.
Hard-to-chew foods
Individuals with Parkinson’s may experience difficulty swallowing and chewing, making it important to avoid such foods. If possible, one must try softening the food by cooking it until it is tender or making soups out of certain ingredients. Additionally, smoothies made from fruits may be a helpful alternative.
Also, working with a speech therapist can be beneficial in managing the swallowing issue. This is caused due to the lack of control over muscle movements, so a speech therapist might be able to help with some exercises.
Processed foods
Foods that are categorized as processed are those that come in packaging and contain artificial flavors and ingredients. Canned foods and regular or zero-calorie sodas are also part of processed foods. These foods affect the gut health and can worsen the symptoms of Parkinson’s, especially the digestive system.
Treatment options
Since there is no cure for the disease, there are only management tips that one can follow, including foods to include and avoid. There are some treatment therapies to help with certain symptoms of the disease, but more research still needs to be done on the overall cure. There are new treatments available that use the compound levodopa, which temporarily replaces the dopamine brain chemical to help with motor symptoms. This includes improvement in tremors, stiffness, and slowness.